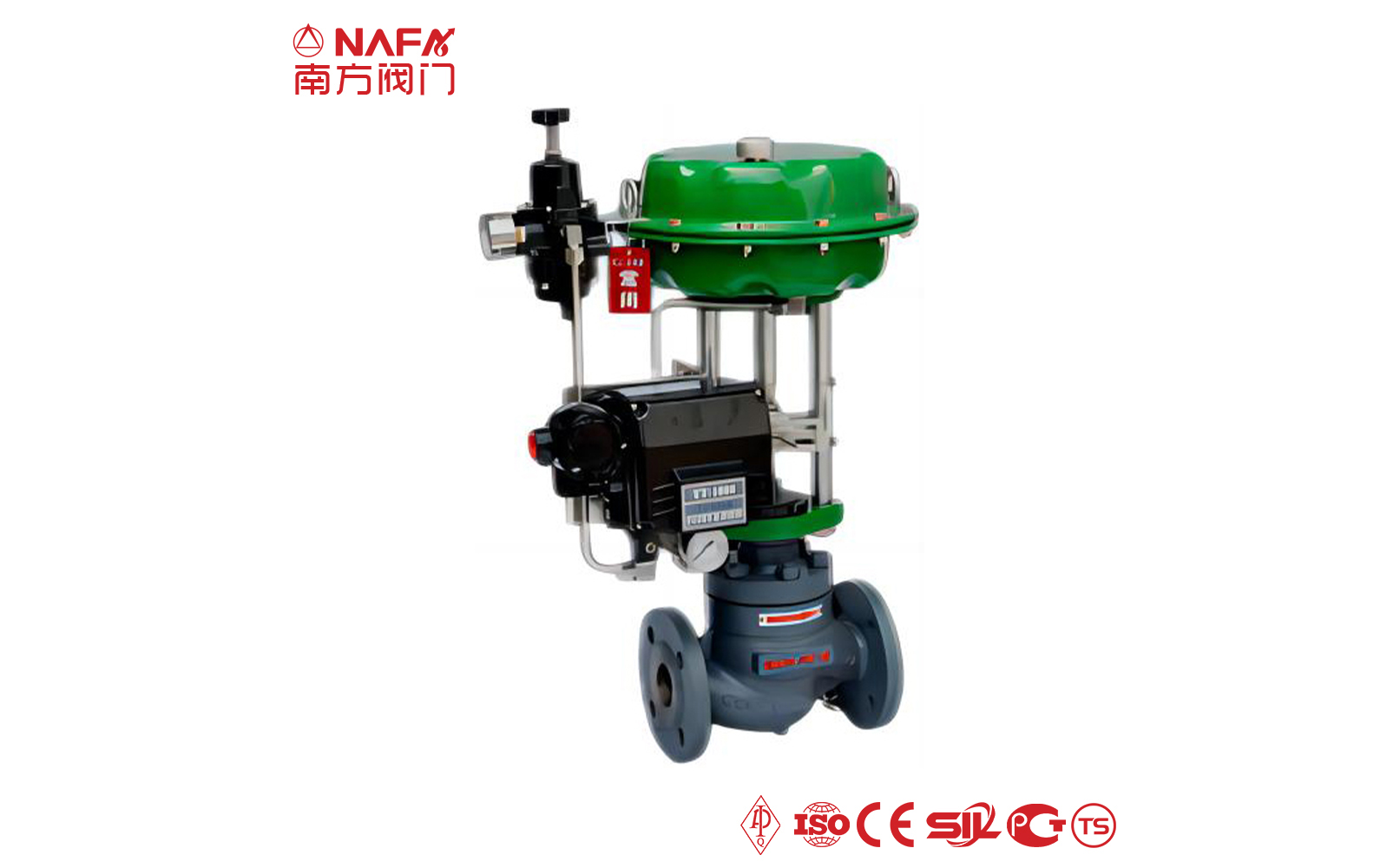
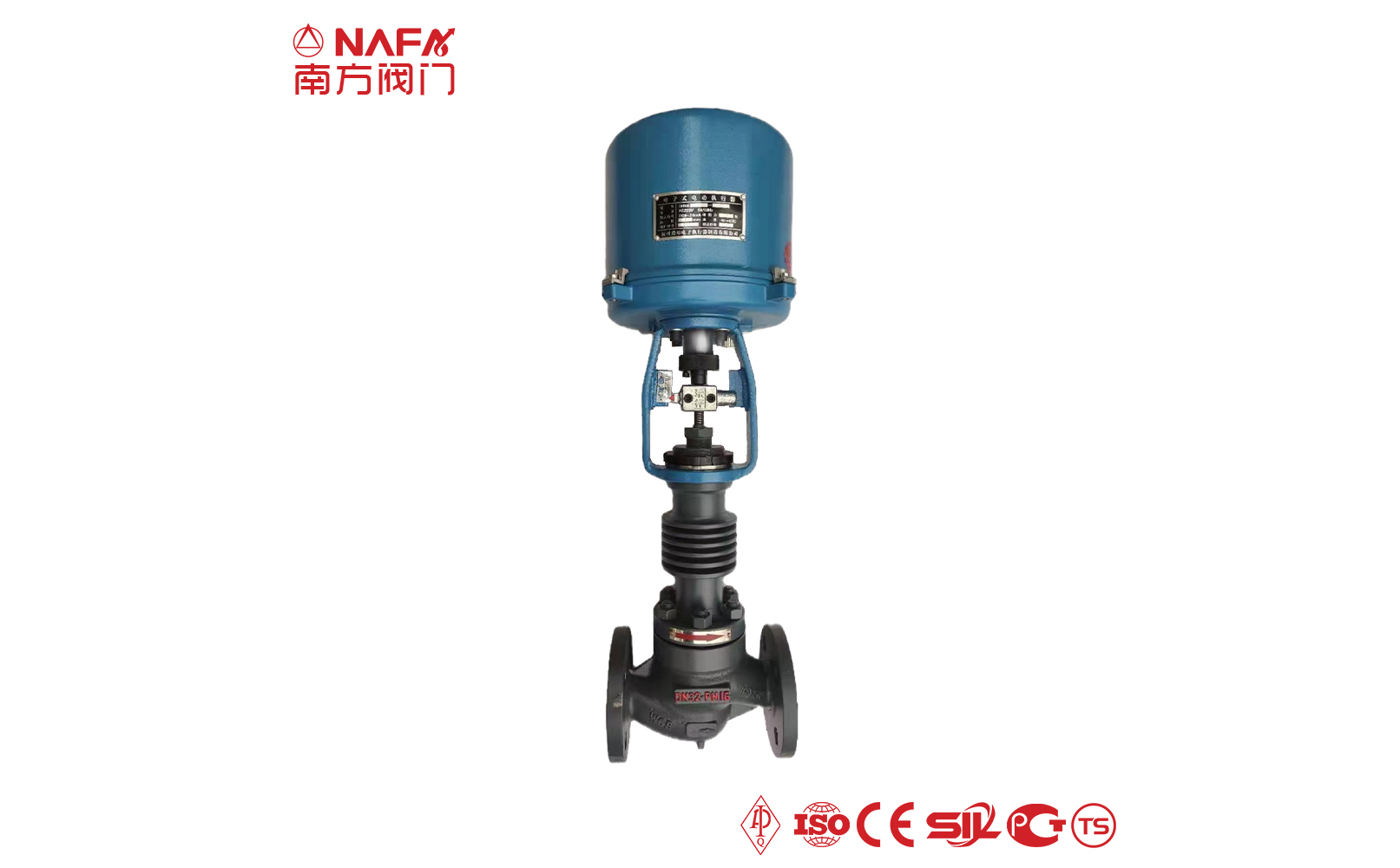
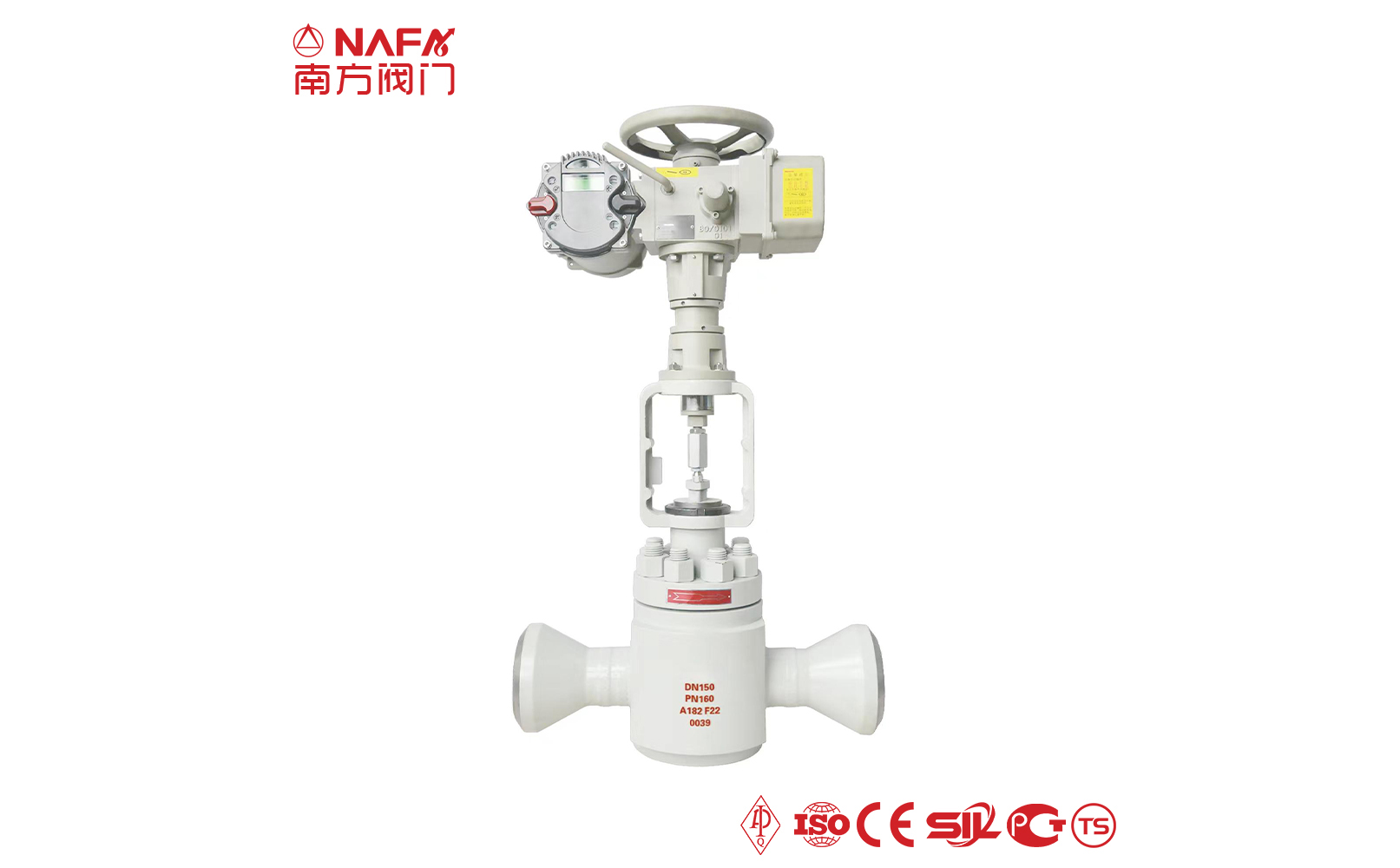
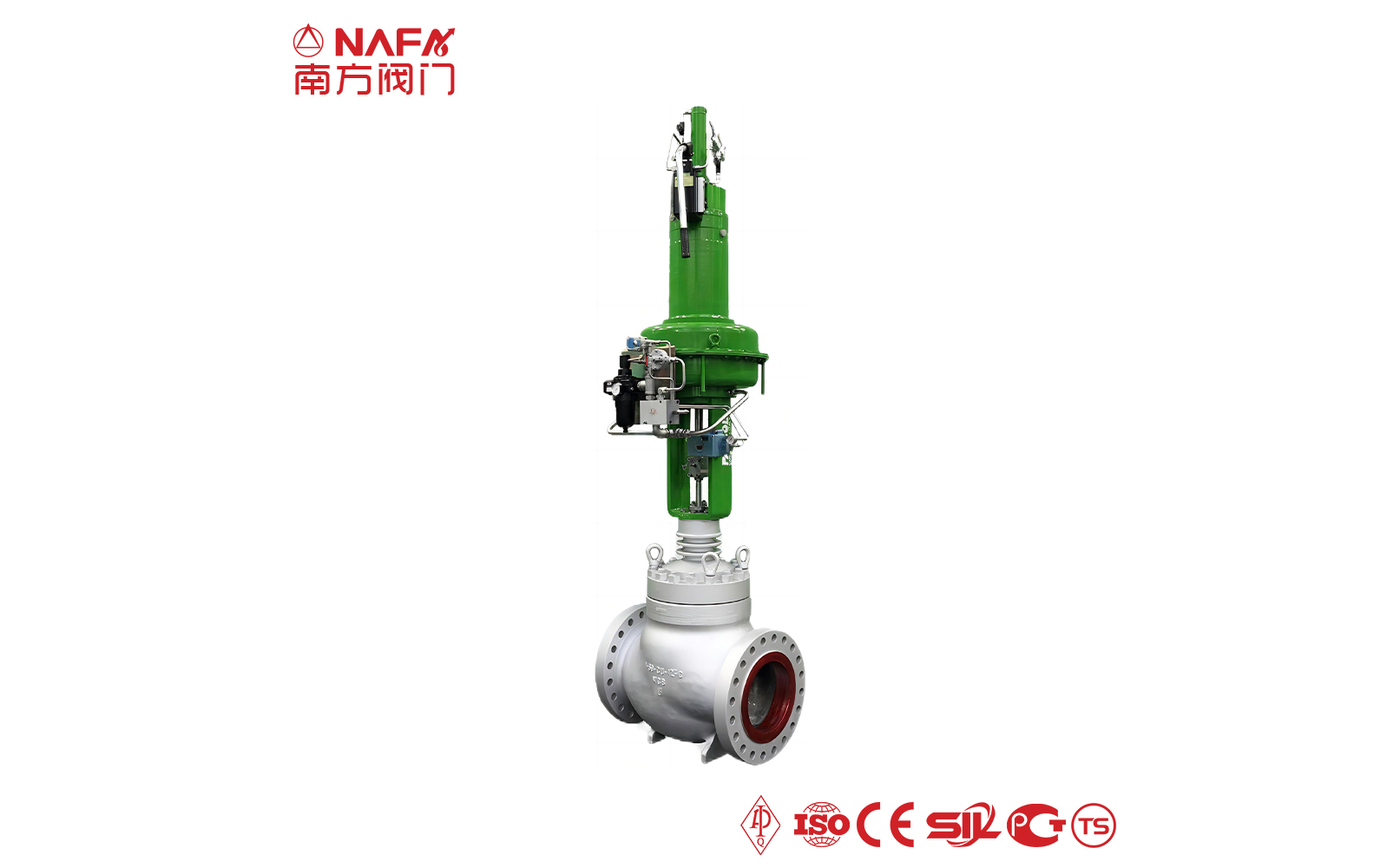
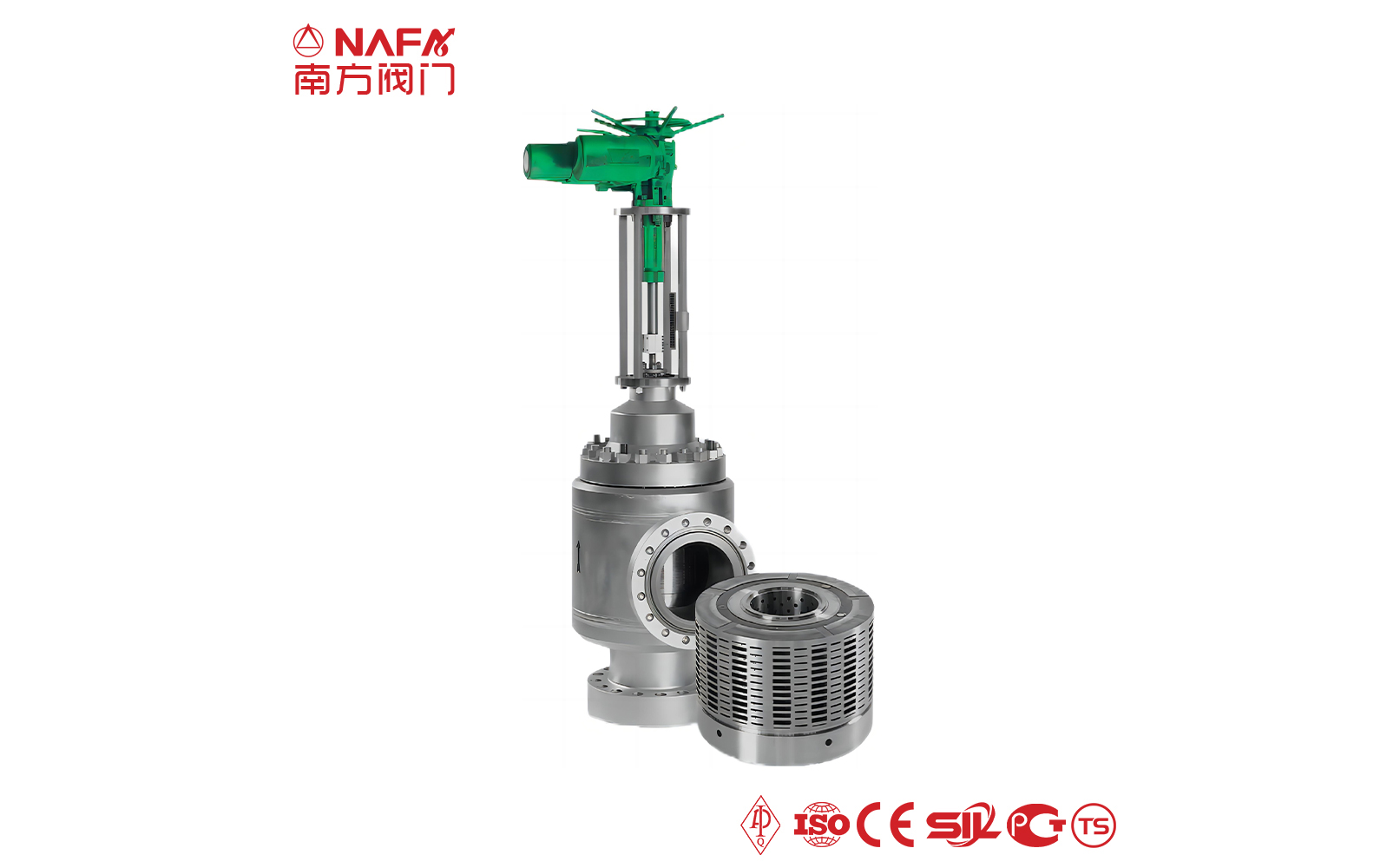
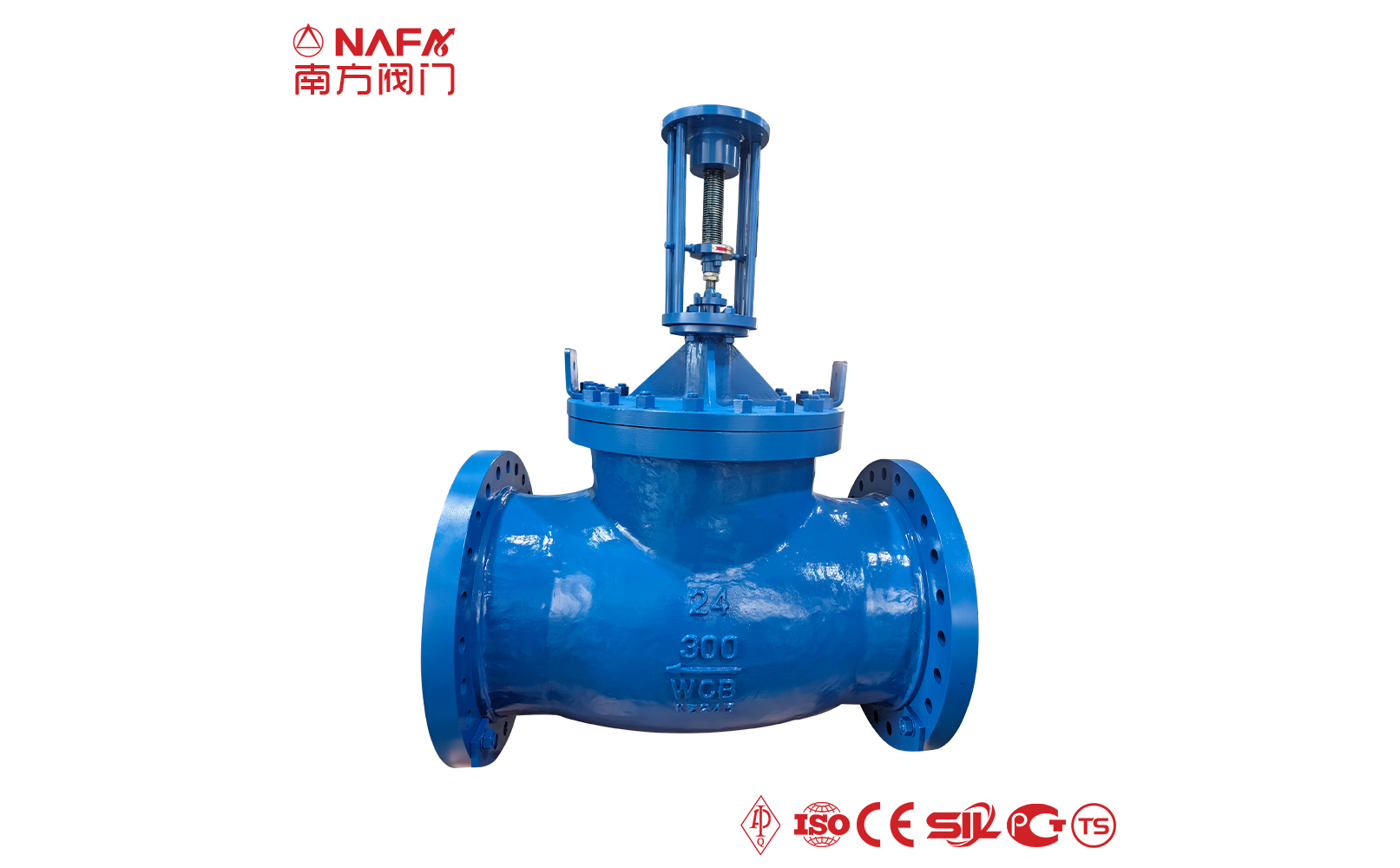
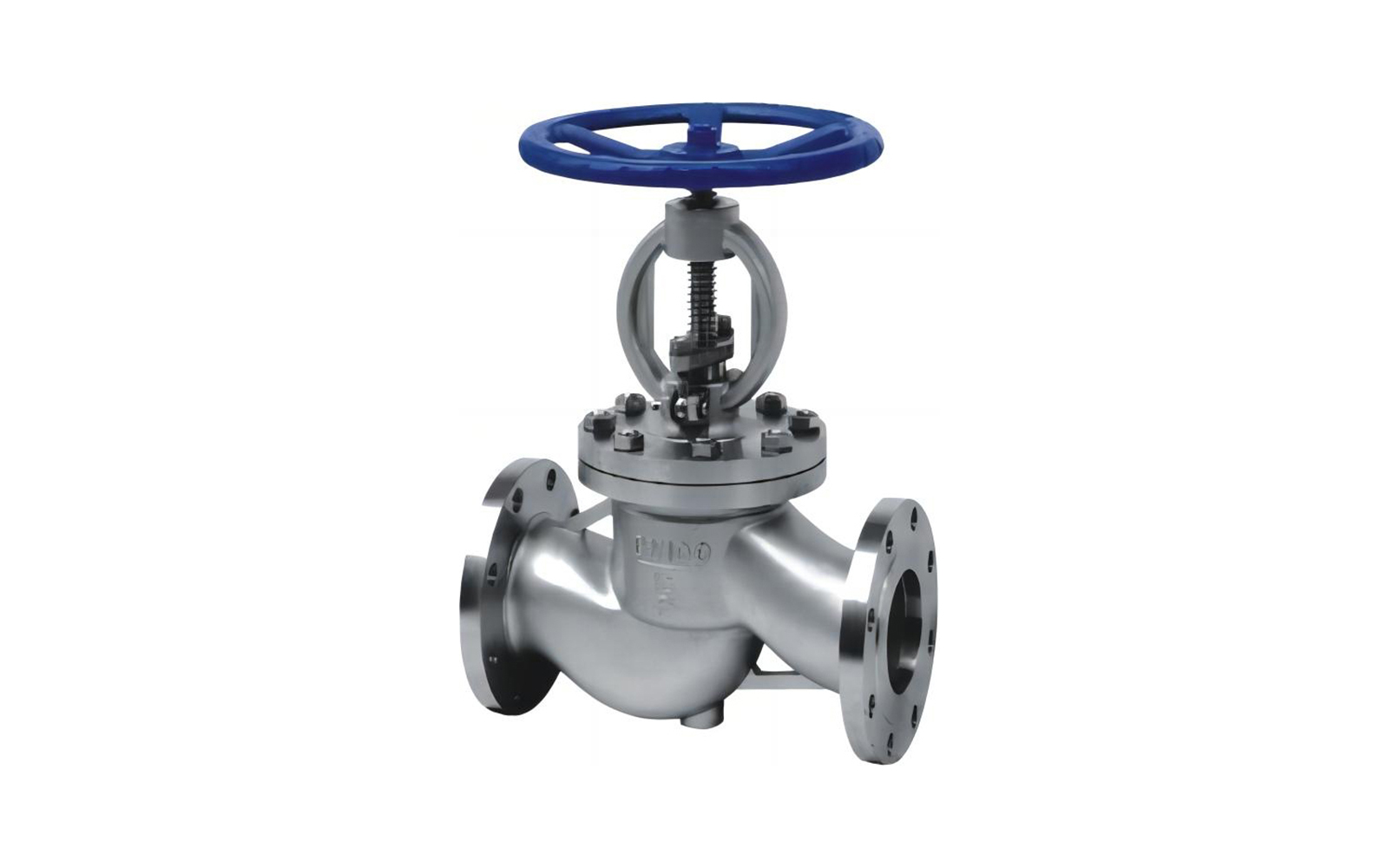
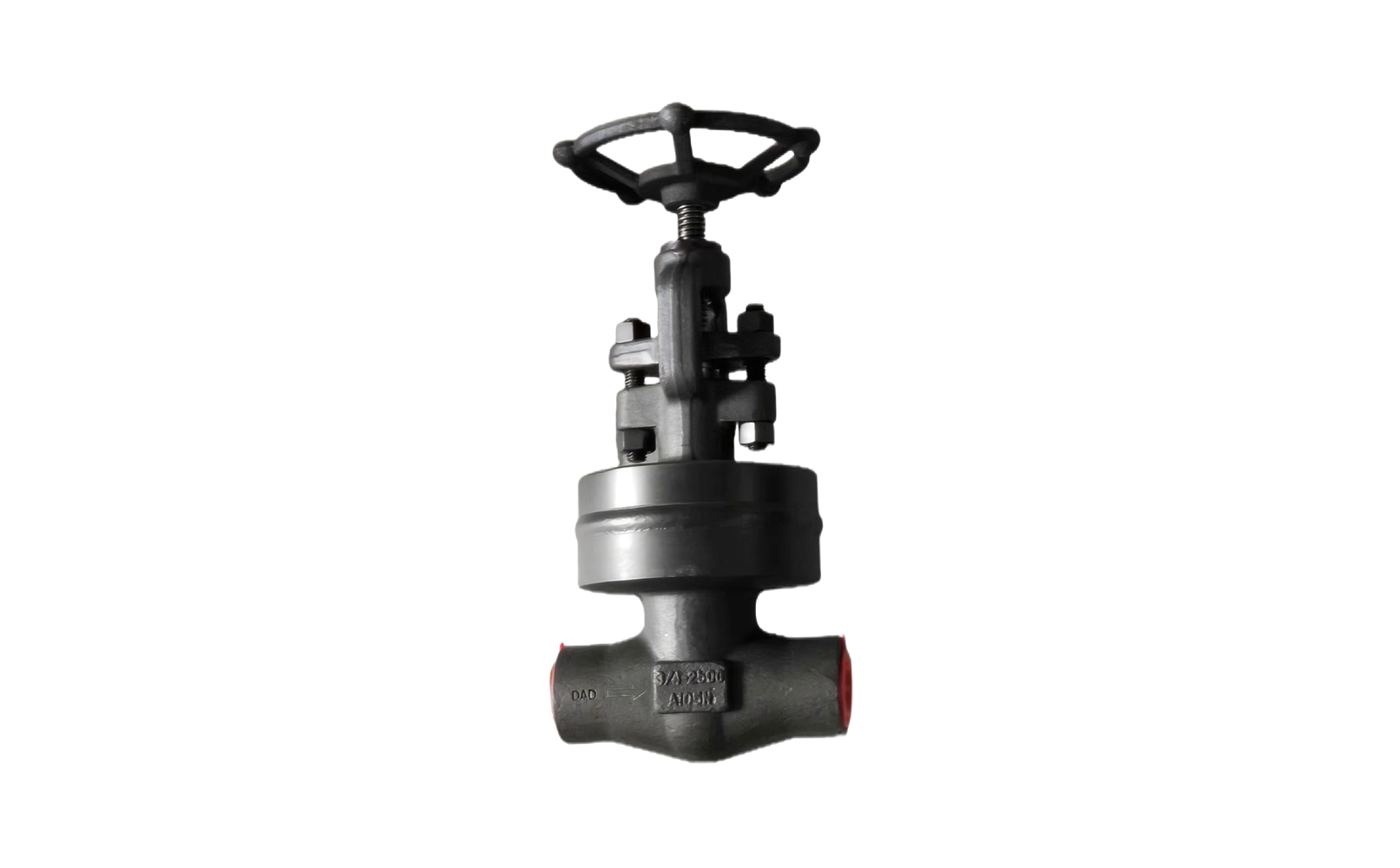
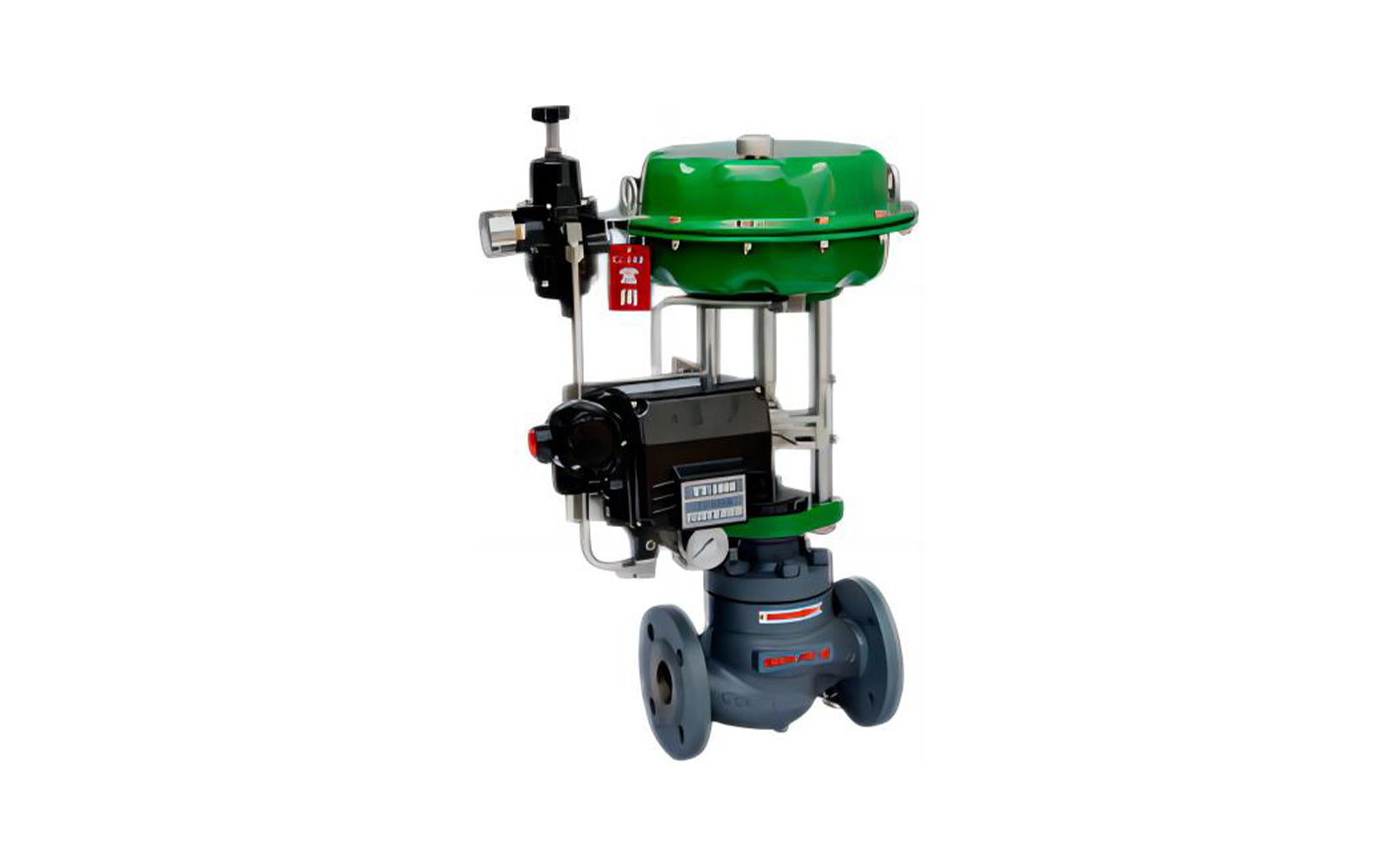
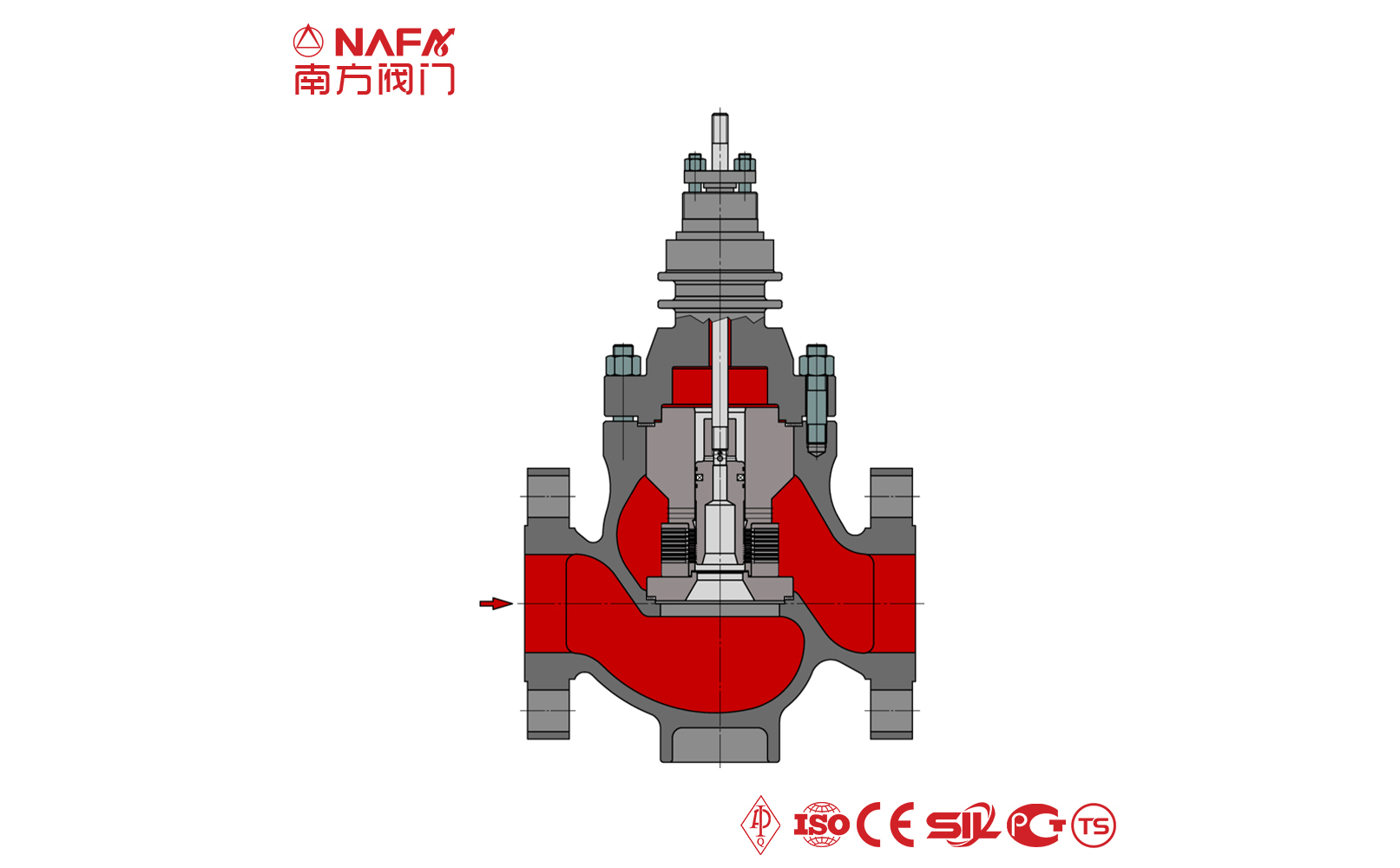
- 01The regulating valve adopts a double bearing structure, with small starting torque, good sensitivity and induction speed; super strong shearing ability.
- 02The pneumatic regulating valve is characterized by simple and convenient operation. The valve can be opened and closed by driving the cylinder through the air source.
- 03The pneumatic regulating valve uses compressed air as the driving source and will not fail to work due to power problems.
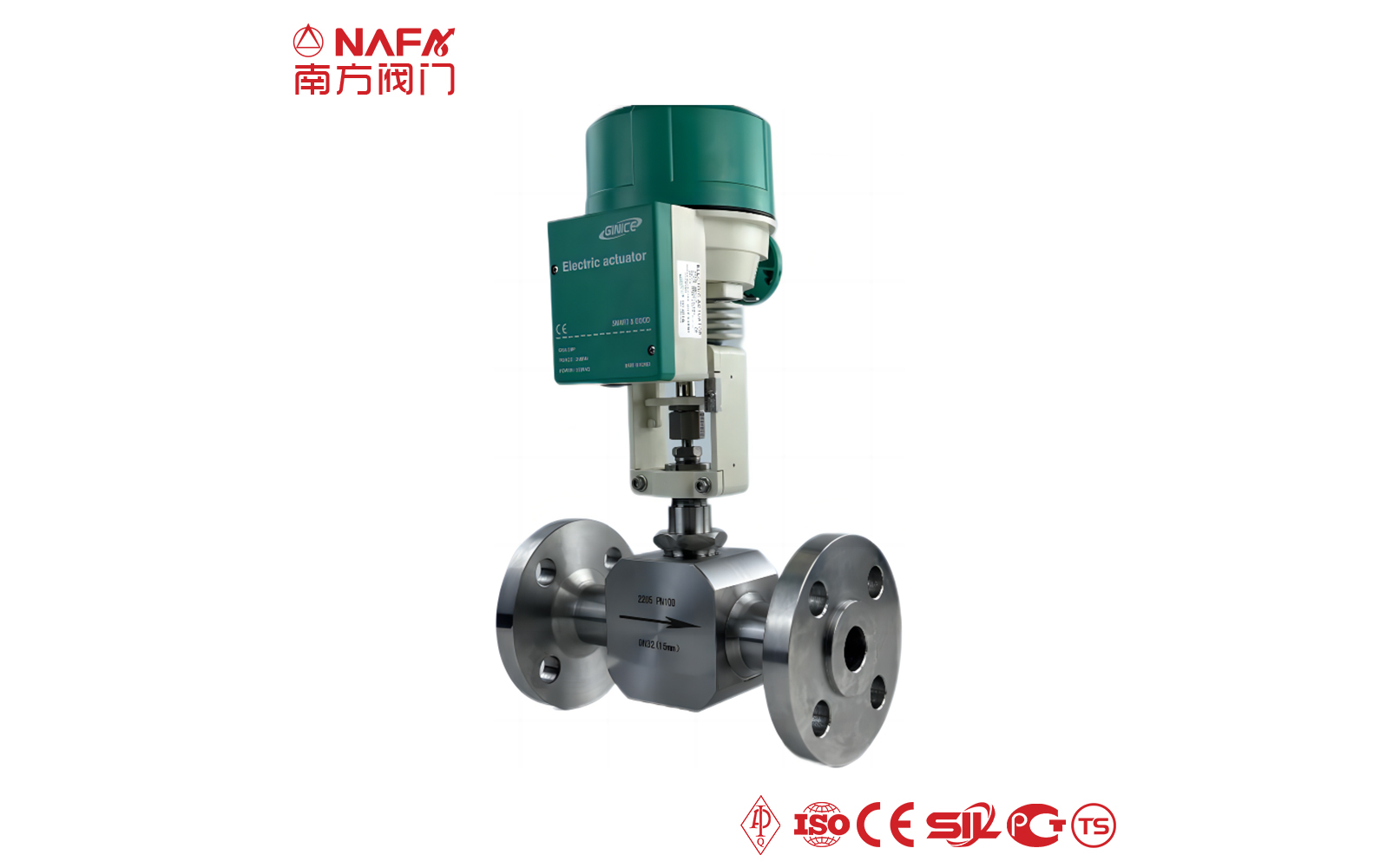
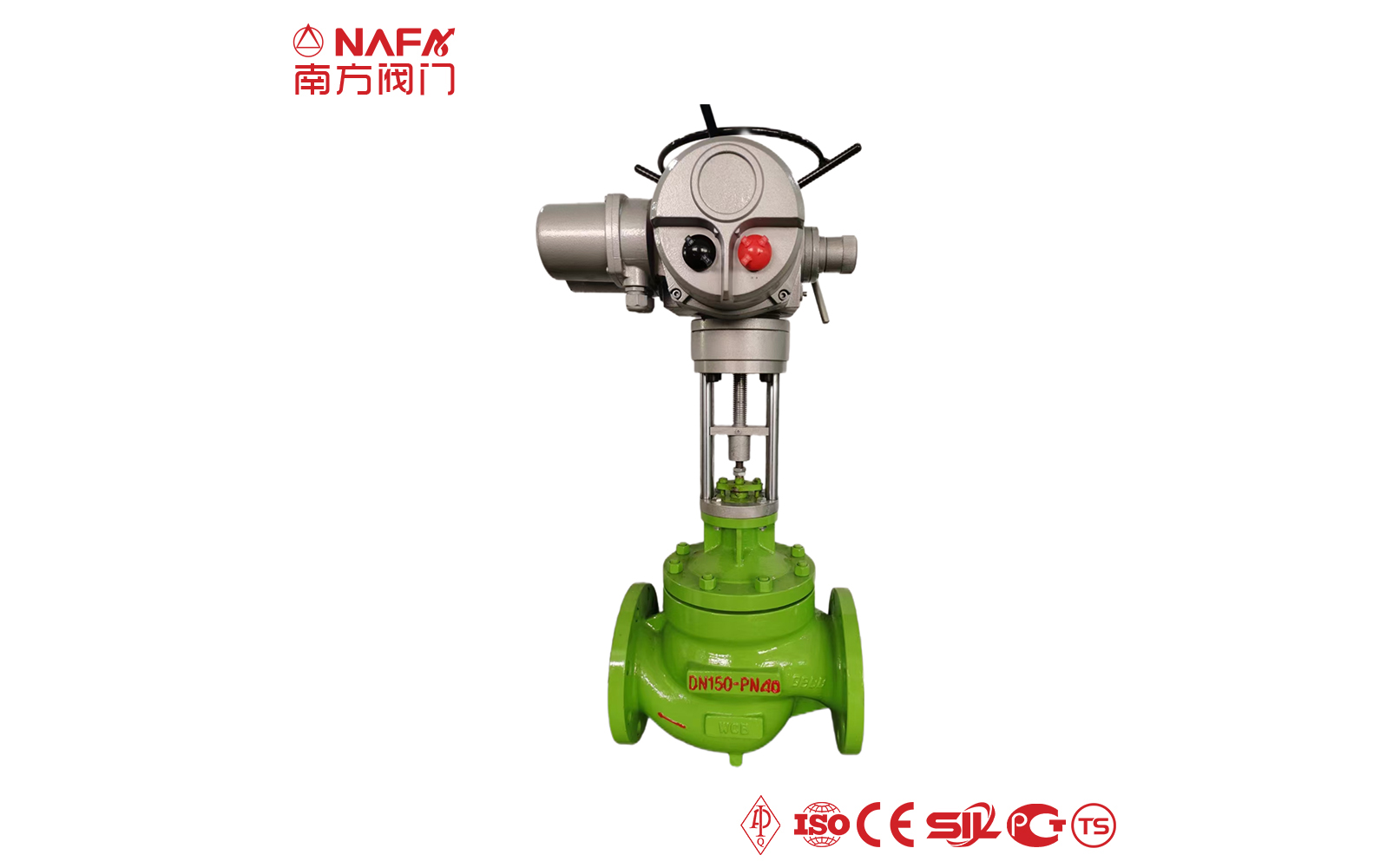
- 04The electric regulating valve adopts a closed-loop control system, which can be accurately adjusted according to the deviation between the set value and the actual value, and has a high adjustment accuracy.
- 05The hydraulic regulating valve has anti-deviation ability, which helps to adjust the working conditions.
- 06The self-acting pressure regulating valve does not require external energy and can work in places without electricity and gas, which is convenient and energy-saving. The pressure segment range is fine and crosses each other, and the adjustment accuracy is high.
-
 API
API -
 АСМЕ
АСМЕ -
 АНСИ
АНСИ -
 RU
RU -
 ДИН
ДИН -
 ГОСТ
ГОСТ -
 ГБ
ГБ -
 JIS
JIS
| TThe characteristics of regulating valve |
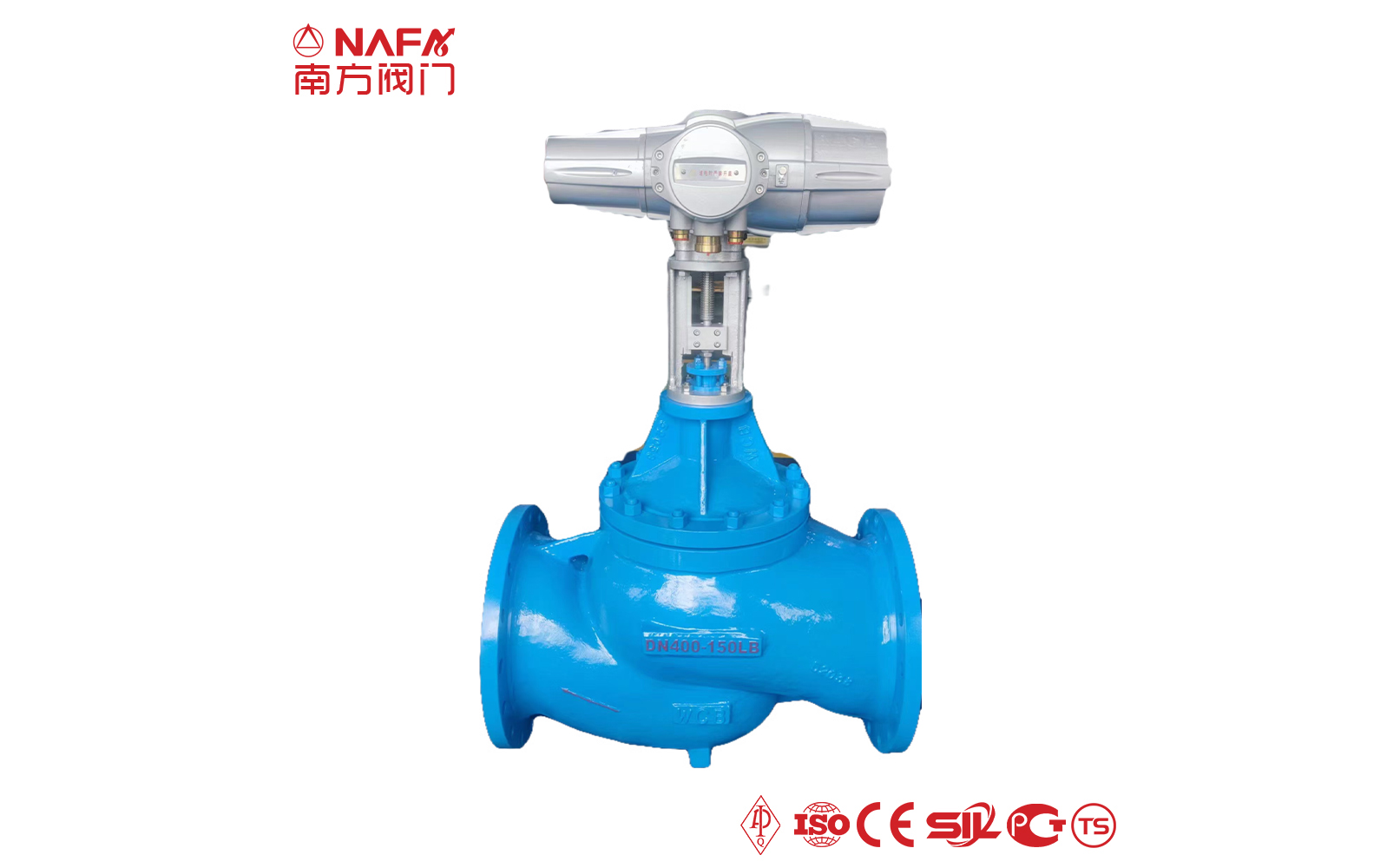
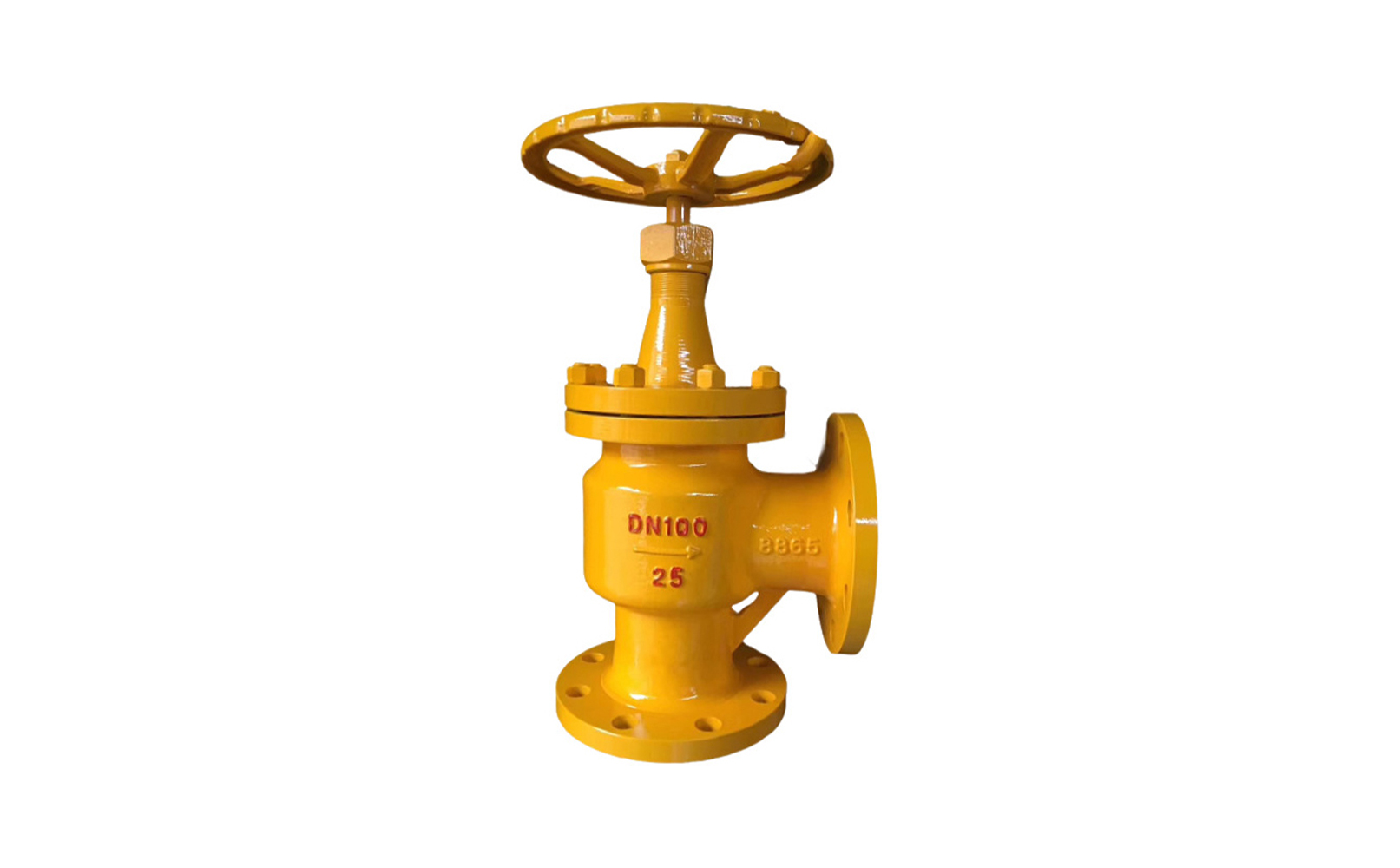
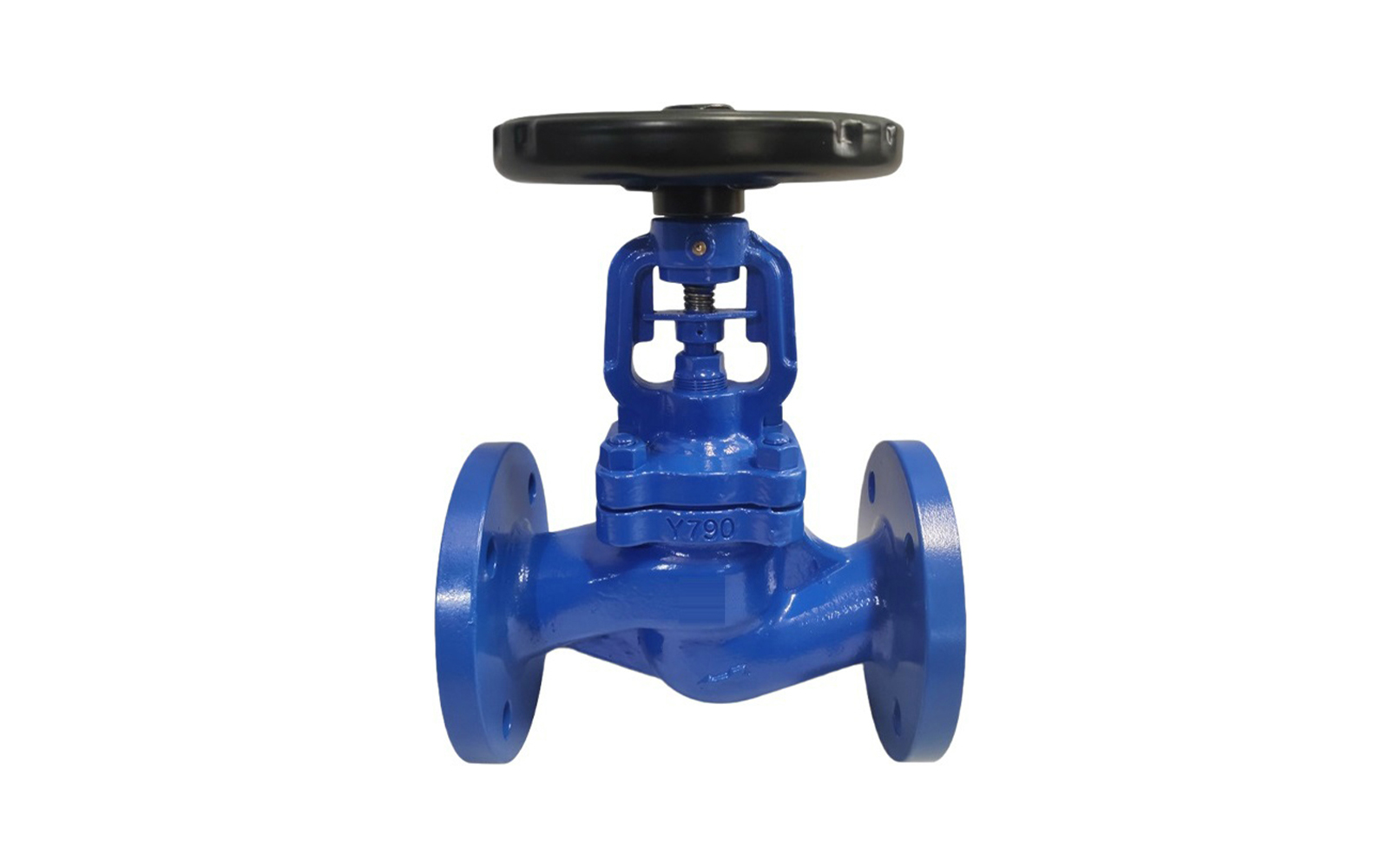
The regulating valve is generally composed of an actuator and a valve. According to the power used by the actuator, the regulating valve can be divided into three types: pneumatic, electric, and hydraulic, that is, pneumatic regulating valves with compressed air as the power source, electric regulating valves with electricity as the power source, and electro-hydraulic regulating valves with liquid medium (such as oil, etc.) pressure as the power source. The regulating mechanism has a straight-through single-seat valve, in which there is only a valve core and a valve seat in the valve body. The valve stem drives the valve core up and down to change the relative position between the valve core and the valve seat, thereby changing the fluid flow. Its main advantage is small leakage. The regulating mechanism has a straight-through double-seat valve, in which there are only two valve cores and valve seats in the valve body. The valve stem drives the valve core up and down to change the relative position between the valve core and the valve seat, thereby changing the fluid flow. Since the fluid pressure acts on the two valve cores, the unbalanced forces offset each other a lot, so the allowable pressure difference is large. The valve body of the sleeve valve is similar to the general straight-through single valve seat, and there is a cylindrical sleeve inside the valve, also called a cage. The valve core can move up and down in the sleeve, guided by the sleeve. The valve core moves in the sleeve, changing the orifice area of the sleeve, forming various characteristics and realizing flow regulation. Since the sleeve valve adopts a balanced valve core structure, it can reduce the unbalanced force of the medium on the valve plug, and with sufficient valve plug guidance, it is not easy to cause the valve core to vibrate. |
| Technical Parameters | |
| Size | DN15-DN1500, 1/2''-60'' |
| Pressure | PN10-PN420, Class150-Class2500 |
| Temperature | -200°C to 650°C |
| Connection Type | Flange, Thread, Wafer, Welded |
| Operation Mode | Manual, Pneumatic, Electric, Hydraulic, Gear operation |
| Materials | ||
| Valve Body | Forged | A105, LF2, F5, F9, F11, F22, F304, F316, F347, F904, F51, F53, F310, N08020, Inconel625, etc |
| Cast | WCB, LCB, C5, C12, WC6, WC9, CF8, CF8M, CF8C, 4A, 5A, CN7M, C95800, CW6MC, etc | |
| Valve Stem | F6a, 17-4PH, XM-19, F304, F316, F347, F904, F51, F53, F310, Monel400, Monel500, N08020, Inconel625, Incoloy825, etc | |
| Valve Disc | A105, LF2, F5, F9, F11, F22, F304, F316, F347, F904, F51, F53, F310, N08020, Inconel625, F6a, 17-4PH, XM-19, F304, F316, F347, F904, F51, F53, F310, Monel400, Monel500,Incoloy825,WCB, LCB, C5, C12, WC6, WC9, CF8, CF8M, CF8C, 4A, 5A, CN7M, C95800, CW6MC, etc | |
| Seat Sealing | SS, BR, CU, AS, CS, AL, PTFE, NBR, FKM, AI203, etc | |
| Design Standards | |
| Valve Body | API 6D, API 608, ASME B16.34, DIN 3357, BS 5351, GOST 9833, JIS B2071, GB/T 12237, etc |
| Flange | ANSI B16.5, EN 1092-1, JIS B2220, GB/T 9113, ASME B16.47, GOST 12821, DIN 2543-2545, etc |
| Connection | ANSI B16.10, ASME B16.25, JIS B2212, GOST 33259, DIN 3202, etc |
| Test Standards | API 598, ISO 5208, BS EN 12266, ASME B16.104, GOST 9544-2015, JIS B2003, DIN 3230, etc |